
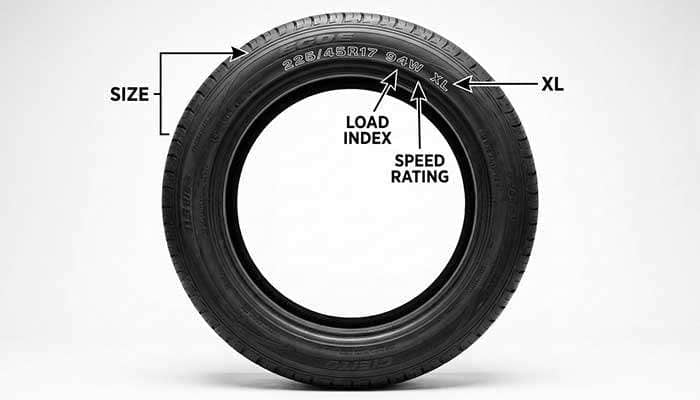
XL load range tires deliver superior load-carrying capability compared to standard tires of identical size. The "XL" designation stands for "eXtra Load" and represents a significant upgrade in tire construction with reinforced internal structure. These enhanced tires handle higher inflation pressures—supporting up to 41-42 PSI versus the 35-36 PSI maximum of standard tires.
The exceptional load-bearing strength of XL tires comes from their robust construction methods. Manufacturers build these tires with strengthened sidewalls and additional reinforcement materials, particularly concentrated in the shoulder area for maximum structural integrity. This reinforced design maintains tire stability under heavy loads while keeping the same external dimensions as standard tires.
You can easily identify XL tires by checking the sidewall markings. Look for "XL," "Extra Load," "Reinforced," or "RF" designations printed on the tire sidewall. These markings confirm the tire's ability to handle additional weight and operate at higher air pressures than standard alternatives.
XL tires provide four key performance advantages:
Support greater weight without tire deformation
Operate safely at elevated inflation pressures
Reduce tire deflection during operation
Minimize damage risk from road impacts
The load capacity relationship is straightforward—XL tires require 0.4 bar higher inflation pressure than standard tires when carrying maximum loads. This increased pressure directly translates to higher load capacity, allowing your vehicle to safely transport heavier cargo or additional passengers.
XL tires maintain identical external dimensions to standard tires of the same size. The difference exists entirely in the internal construction—the reinforced structure that enables these tires to withstand greater stress and pressure.
Most passenger vehicles including sedans, coupes, and minivans function perfectly with standard load tires. However, vehicles that regularly carry heavy loads or need extra stability benefit significantly from XL-rated tires.
XL tires cost more than standard equivalents, but their superior durability typically provides longer service life, especially under demanding conditions. The reinforced structure allows these tires to travel greater distances without internal damage during intense use, provided you maintain proper inflation pressure. XL tires also demonstrate better resistance to mechanical damage and handle the pressures of high-speed driving more effectively.
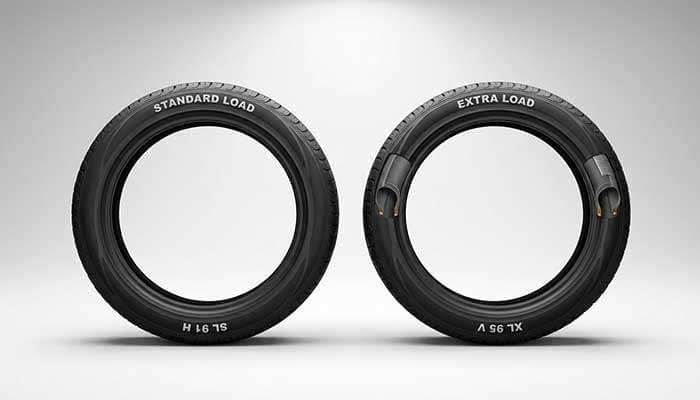

Standard Load and Extra Load tires represent two distinct approaches to tire construction and performance capabilities. Understanding these differences helps you select the right tire for your specific vehicle needs and driving conditions.
Standard Load tires feature conventional construction designed for everyday passenger vehicle use. These tires operate at a maximum pressure of 35 psi and handle the typical loads encountered in daily driving. Most sedans, coupes, and compact cars come equipped with SL tires from the factory, often marked simply with "SL" on the sidewall or carrying no special designation.
Extra Load tires incorporate additional reinforcement materials throughout their construction, particularly in the shoulder areas. This enhanced structure allows them to safely handle pressures up to 41 psi, creating significantly higher load-carrying capacity. The reinforcement also reduces tire deflection and improves resistance to road impact damage.
The structural differences create distinct performance characteristics:
Load Capacity: XL tires support substantially more weight than SL tires of identical size
Pressure Range: XL tires safely operate at higher pressures (41 psi maximum vs. 35 psi)
Service Life: XL construction typically delivers longer tread life under demanding conditions
Damage Resistance: Enhanced protection against mechanical damage from road hazards
However, Standard Load tires offer their own advantages. The lighter construction generally provides better fuel economy and delivers a smoother, quieter ride quality compared to the firmer feel of XL tires.
Vehicle type largely determines which load range works best for your needs. Standard Load tires suit sedans, compact cars, and vehicles used primarily for commuting and everyday driving. Extra Load tires match well with SUVs, light trucks, and any vehicle that regularly carries heavy cargo or tows trailers.
Proper load range selection prevents serious problems. Using SL tires beyond their pressure limits can result in tire damage, handling issues, or dangerous blowouts. This makes matching your tire choice to your actual vehicle requirements and usage patterns essential for both safety and performance.
The structural differences between XL and standard load tires create measurable impacts on your vehicle's performance. Understanding these changes helps you make the right choice for your specific driving needs.
XL tires operate at higher inflation pressures, supporting up to 41 psi compared to the 35 psi maximum for standard load tires. This pressure difference directly enables the increased load-bearing capacity. The relationship between air pressure and load support is fundamental—your tire's ability to carry weight depends primarily on proper inflation pressure.
When both SL and XL tires are inflated to identical pressures up to 35 psi, they actually support the same loads. The XL advantage emerges when you inflate beyond standard pressure limits, allowing these reinforced tires to bear substantially more weight.
This pressure-weight relationship becomes critical for heavy-duty applications:
XL tires require 0.4 bar higher inflation pressure than standard tires at maximum load
Underinflated tires will fail under heavy loads, regardless of their construction
The superior performance of XL tires comes from their reinforced internal architecture. These tires feature additional fabric or steel layers alongside strengthened sidewalls. This fortified construction allows XL tires to maintain their proper shape even under heavy loads.
The reinforcements throughout the tire structure—especially in the sidewall and shoulder areas—minimize deflection under intense pressure. XL tires typically deliver longer service life than standard tires when used under identical conditions. Their enhanced resistance to mechanical damage makes them particularly well-suited for high-speed driving applications.
XL tires can travel longer distances without internal damage, even during intense use, provided you maintain proper inflation pressure. This damage resistance stems from their ability to limit tire deflection when hitting road impacts.
The same reinforced structure that provides XL tires their load capacity and durability affects your driving experience. The stiffer construction typically delivers a firmer ride compared to standard load tires. This increased rigidity often transmits more road feedback to passengers.
XL tires produce more road noise than their standard counterparts. The additional reinforcement materials increase tire weight, creating slightly higher rolling resistance that can impact fuel economy. Many drivers find these trade-offs acceptable when their vehicle requires the extra load capacity.
For vehicles that don't need additional load capacity, standard tires often provide a more comfortable driving experience with better fuel efficiency. Your choice between SL and XL ultimately depends on balancing performance requirements against comfort preferences.
Choosing the right tire load range depends on your specific vehicle needs and driving conditions. XL tires become the smart choice when standard load tires simply can't deliver the performance and safety your vehicle demands.
Vehicles with substantial curb weight typically require XL tires to operate safely and efficiently. SUVs, crossovers, and light trucks naturally benefit from XL tires because these vehicles weigh considerably more than standard passenger cars. The reinforced construction enables them to handle this additional weight without compromising performance or safety.
Many vehicle manufacturers specifically recommend XL tires for heavier models to properly support the vehicle's own weight before you even add cargo or passengers. Heavy-duty trucks, commercial vehicles, and buses rely on XL tires with reinforced sidewalls precisely because their substantial weight demands this extra structural support. Standard tires simply cannot provide the necessary load-bearing capacity these vehicles require.
When you regularly engage in towing or hauling heavy loads, XL tires offer crucial advantages that standard tires cannot match. Light trucks transporting substantial cargo or pulling trailers need tires capable of supporting this additional weight safely. The higher pressure capacity of XL tires—up to 41 psi versus the 35 psi limit of standard tires—directly translates into superior load-bearing performance.
Proper tire inflation becomes absolutely critical during towing operations. Underinflated tires flex excessively, creating dangerous heat buildup, accelerated tread wear, and increased blowout risk. XL tires provide the necessary structural integrity to handle these demanding conditions when properly inflated to their higher pressure specifications.
Performance vehicles commonly use XL tires even without heavy load requirements. The reinforced internal structure and specialized compounds deliver superior traction and durability during high-speed operation. This enhanced construction maintains proper tire shape under the intense forces generated during performance driving.
XL tires improve steering responsiveness and driving stability at high speeds through their reinforced structure and optimized contact patch. Their superior heat distribution capabilities across the tread area provide additional safety margins during demanding driving conditions.
XL tires deliver specific benefits that make them valuable for certain driving situations, though they also present some tradeoffs worth considering.
The enhanced load capacity stands as the primary advantage of XL tires. These tires support significantly more weight than standard versions of the same size, making them essential for heavy vehicles and cargo hauling. Their reinforced construction provides exceptional resistance to road hazards, curbs, and impact damage that would compromise standard tires.
XL tires deliver superior stability and handling characteristics. The reinforced structure creates better traction and grip properties, resulting in improved cornering behavior and more responsive steering. This enhanced performance becomes especially valuable during demanding driving conditions.
Durability represents another key strength of XL tires. Their robust internal structure typically provides longer service life, particularly when used under challenging conditions. When compared directly to standard tires under identical usage, XL variants consistently demonstrate extended tread life. The reinforced design maintains performance and stability even during high-speed driving scenarios.
XL tires generate more road noise than standard alternatives. Industry regulations actually permit XL tires to produce 1 dB higher noise levels than standard versions. The additional reinforcement materials increase overall weight and thickness, particularly in the crown and shoulder areas, which contributes to higher rolling resistance and reduced fuel economy.
Ride comfort differs noticeably with XL tires. The stiffer construction creates a firmer ride experience compared to the smoother feel of standard load tires. While many drivers find these comfort differences minimal, those prioritizing the smoothest possible ride may prefer standard alternatives.
Cost considerations also factor into the decision. XL tires command higher prices than comparable standard tires. However, their extended durability often offsets the initial price premium, especially for vehicles that regularly operate under demanding conditions.
Understanding XL load range tires helps you make informed decisions about vehicle safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness based on your specific driving needs.
• XL tires support 41 PSI vs 35 PSI for standard tires, enabling significantly higher load capacity through reinforced internal construction • Choose XL tires for heavy vehicles, frequent towing, or high-speed driving where extra load capacity and durability are essential • XL tires offer superior durability and longer tread life but sacrifice ride comfort with firmer handling and increased road noise • Standard Load (SL) tires provide better fuel economy and smoother rides for everyday passenger vehicles without heavy load requirements • Proper inflation is critical—XL tires require 0.4 bar higher pressure than standard tires when carrying maximum loads
The key decision factor is matching tire type to your vehicle's actual usage: XL for demanding conditions, SL for comfortable daily driving.
XL load range indicates tires designed to carry heavier loads than standard tires of the same size. These tires have a reinforced internal structure that allows them to support higher inflation pressures, typically up to 41-42 PSI compared to the 35-36 PSI limit of standard tires.
SL (Standard Load) tires are designed for everyday driving conditions with a maximum load pressure of 35 PSI. XL (Extra Load) tires have a reinforced structure, can handle higher pressures up to 41 PSI, and support greater load capacity. XL tires are generally more durable but may provide a firmer ride compared to SL tires.
XL tires are recommended for vehicles with heavy curb weight (such as SUVs and light trucks), those frequently used for towing or carrying heavy cargo, and high-performance vehicles. They're also suitable for situations requiring enhanced stability and durability, especially during high-speed driving.
Yes, XL tires typically require higher inflation pressures than standard tires. When carrying a full load, XL tires need about 0.4 bar (approximately 5.8 PSI) higher inflation pressure than standard tires. Always refer to your vehicle's manual and the tire manufacturer's recommendations for precise inflation guidelines.
Pros of XL tires include higher load capacity, improved durability, better resistance to mechanical damage, and enhanced stability during high-speed driving. Cons include potentially higher road noise, slightly increased fuel consumption due to greater rolling resistance, a firmer ride quality, and typically higher purchase costs compared to standard tires.