
Replacing trailer wheels shouldn't be a guessing game. When wheels don't fit properly, you're looking at safety risks and wasted money. Understanding trailer wheel fitment helps you select the right wheels every time.
The bolt pattern determines everything when it comes to wheel compatibility. Trailers with 4 bolt holes commonly use 4 on 4 and 4 on 9.44 patterns, while 6-bolt configurations typically feature a 6 on 5-1/2 pattern. For heavy-duty applications, you'll find 8-bolt patterns like 8 on 6-1/2 or 8 on 275mm. The first number in a bolt pattern tells you how many lug holes exist, and the second number shows the diameter of the circle those holes create.
Bolt pattern matching is just the starting point. Your trailer's rim and tire combination must work together for safe towing performance. A trailer with a 4 on 4 inch bolt pattern requires replacement wheels with exactly that same pattern. You'll also encounter other standard configurations including 5 on 4.5, 5 on 5, 6 on 5.5, and 8 on 6.5.
Getting the right wheels means understanding how to measure bolt patterns accurately, knowing what size requirements matter, and recognizing the other factors that affect proper fit. Whether you're replacing damaged wheels or upgrading your trailer setup, this information ensures you make the correct choice from the start.
Proper wheel selection for your trailer goes beyond appearance—it directly impacts safety and towing performance. At Performance Plus Tire, we know that understanding fitment basics prevents costly mistakes and dangerous situations.
Wheel fit means complete compatibility between your trailer's wheels and axle hubs. This compatibility covers bolt pattern, wheel size, load rating, and center bore diameter. Miss any of these specifications and you risk wheel failure or safety hazards.
When we talk about wheels, we mean the complete rim and tire assembly. Your replacement wheels must match your trailer's specifications exactly to maintain proper weight distribution and stability. Incorrect wheel sizing causes uneven trailer positioning, creating inefficient towing conditions and potential handling problems.
Hub-centric wheels center themselves on the hub, while lug-centric wheels center when you tighten the lug nuts to proper torque specifications. This difference determines your lug nut type—flange nuts work with hub-centric wheels, while cone nuts pair with lug-centric designs.
The bolt pattern combines two essential measurements: lug hole count and circle diameter. Without an exact match to your trailer's hub configuration, the wheel cannot attach properly.
Smaller trailers commonly use 4-lug or 5-lug patterns, while heavy-duty applications require 6-lug or 8-lug configurations. More lugs typically indicate higher weight capacity—a direct relationship between bolt pattern and trailer capability.
Rim size affects tire compatibility significantly. A 205/75-15 tire works with rim widths from 5 to 6-1/2 inches, but a 225/75-15 tire fits only 5 to 6-inch widths. Precise specification matching ensures proper tire seating and optimal performance.
Trailer wheels range from 13 to 16 inches in diameter. Here are the most common sizes and their compatible tire options:
| Wheel Size | Compatible Tire Sizes |
|---|---|
| 13x4.5 | ST155/80D13, 165R13 |
| 13x4.5, 13x5 | ST175/80D13, ST175/80R13, ST185/80D13 |
| 14x5.5, 14x6 | ST195/75D14, ST205/75D14, ST205/75R14 |
| 15x5, 15x6 | ST205/75D15, ST205/75R15 |
| 15x6, 15x7 | ST225/75D15, ST225/75R15 |
Steel and aluminum represent the two main wheel materials. Steel wheels offer lower initial cost but add weight and require more maintenance due to rust susceptibility. Aluminum wheels resist corrosion better, dissipate heat more effectively, and can reduce weight by up to 30 pounds—improving your fuel efficiency. However, aluminum wheels typically cost two to three times more than steel alternatives.
Load range ratings (B, C, or D) indicate the maximum weight each tire safely supports. Higher load ranges provide greater capacity and pressure ratings. Load Range B equals the former 4-ply rating, C equals 6-ply, and D equals 8-ply. A Load Range D tire handles more weight than the same size tire with Load Range C.
Mastering these fitment fundamentals helps you choose the right wheels for your trailer needs, ensuring safe and efficient towing performance every time.

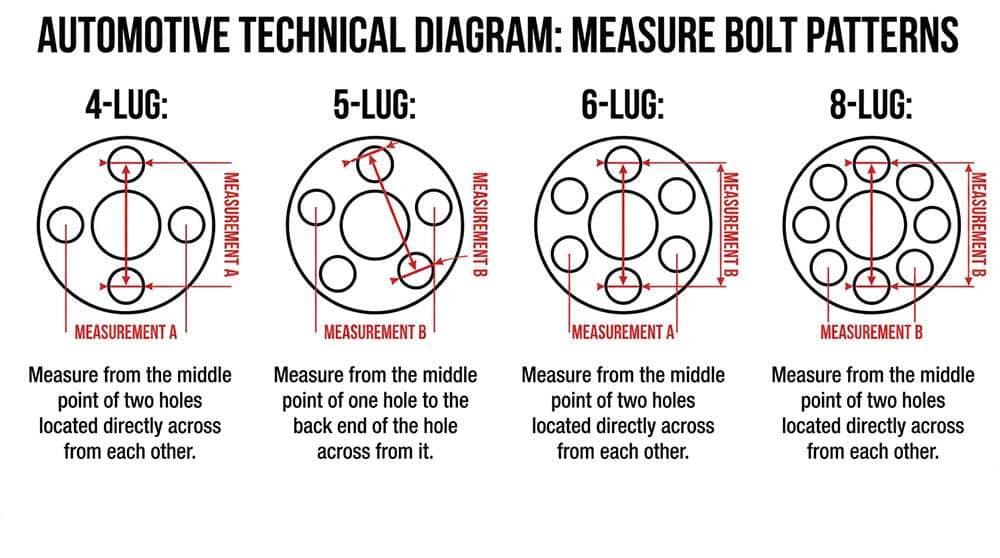
Getting your trailer's bolt pattern measurement right makes the difference between wheels that fit perfectly and wheels that don't fit at all. The bolt pattern combines two essential measurements: the number of lug holes and the diameter of the circle they form.
Start by counting the lug holes (or studs) on your trailer wheel. Most trailers use 4 or 5 lugs per wheel, though heavy-duty trailers often have 6 or 8 lugs for additional weight capacity. This count becomes the first number in your bolt pattern - like "5 on 4.5" for a wheel with 5 lugs arranged on a 4.5-inch diameter circle.
Trailers typically follow these standard configurations:
4-lug patterns: Usually 4 on 4 inches
5-lug patterns: Most commonly 5 on 4.5 inches (sometimes written as "545")
6-lug patterns: Generally 6 on 5.5 inches
8-lug patterns: Often 8 on 6.5 inches
For wheels with an even number of lugs, measuring bolt pattern is straightforward. Take a ruler or caliper and measure straight across from the center of one stud to the center of the directly opposite stud. This center-to-center measurement gives you the circle diameter - the second number in your bolt pattern.
For example, if you measure 4.5 inches across on a wheel with 4 lugs, your bolt pattern is "4 on 4.5". Make sure you measure from the precise center of each stud for accuracy - even small variations can prevent proper wheel fitment.
Five-lug patterns require a different approach since no stud sits directly across from another. Use the center-to-edge method: measure from the center of one stud to the outer edge of the hole farthest away. This measurement gives you the circle diameter.
For greater precision, use the adjacent bolt method: measure from the center of one stud to the center of the adjacent stud, then multiply by 1.701. For example, if adjacent studs are 2.65 inches apart, multiply by 1.701 to get a 4.5-inch bolt pattern (5 on 4.5).
A bolt pattern gauge simplifies this process - these tools feature pre-marked circles that match standard patterns. Place the gauge on your hub and see which circle aligns with your studs. This eliminates calculation errors and works for any lug count.
Double-check your measurements using multiple methods when possible. If your manual measurement shows 5 on 4.5 inches and a bolt pattern gauge confirms it, you can trust the result. Always measure in inches for trailer applications - metric measurements can cause confusion.
Common trailer bolt patterns include:
4 on 4 inches
5 on 4.5 inches (most popular)
5 on 5 inches
6 on 5.5 inches
8 on 6.5 inches
Record your measurements and keep them with your trailer documentation. This information saves time when purchasing replacement wheels and helps avoid ordering mistakes.
Bolt pattern matching ensures your wheel bolts to your hub, but several other specifications determine whether your wheels actually work with your trailer. Missing any of these measurements creates safety hazards or performance problems.
The center bore (or hub bore) is the large hole at the wheel's center that slides over your trailer's hub. This measurement must be exact - too small and the wheel won't fit over the hub, too large and you'll experience vibrations and premature wear.
Hub-centric wheels rely on the center bore for proper alignment, while lug-centric wheels center themselves when you tighten the lug nuts. Most trailer wheels use lug-centric designs with cone-shaped lug nuts that center the wheel as you tighten them.
Always verify your trailer's hub diameter before ordering wheels. The center bore specification appears on your existing wheels or in your trailer's documentation.
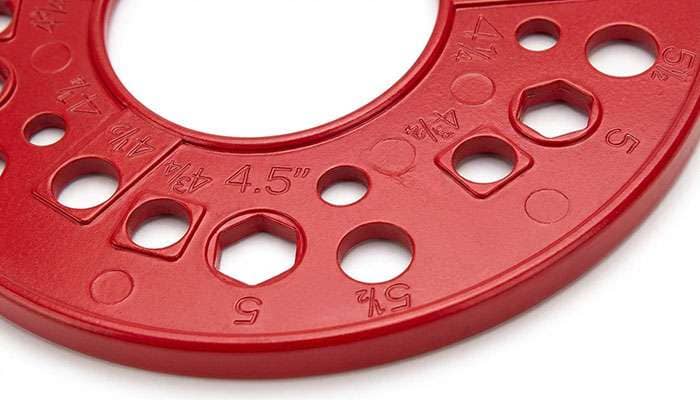
Rim diameter represents the distance across the wheel at the point where the tire bead seats against the rim. For width, measure from one bead seat to the opposite bead seat, not from the outer edges. A "14 X 5-1/2" wheel means 14-inch diameter and 5.5-inch width.
Pay attention to rim contour markings. You'll find stamps like "JJ" or "K" on your wheel that indicate the rim shape where the tire meets the wheel. Match your existing profile or check your trailer's VIN plate for the correct specifications.
Offset measures the distance between the wheel's centerline and mounting surface, typically shown in millimeters. Positive offset moves the wheel closer to the suspension, while negative offset pushes it outward toward the fender.
Backspacing tells a different story - it's the distance from the mounting hub to the wheel's inner lip, measured in inches. This measurement determines clearance between the wheel's inner surface and brake components. Get backspacing wrong and you'll have clearance problems with suspension or fenders.
Yes, trailer wheels benefit from balancing despite what you might hear. Unbalanced trailer tires don't affect ride comfort as much as car tires, but they significantly impact tire life and safety. Balanced tires run cooler and smoother, reducing blowout risks while improving fuel efficiency.
When installing new tires on your rims, consider balancing them with a pin plate adapter that mimics how lug-centric wheels mount to the hub.
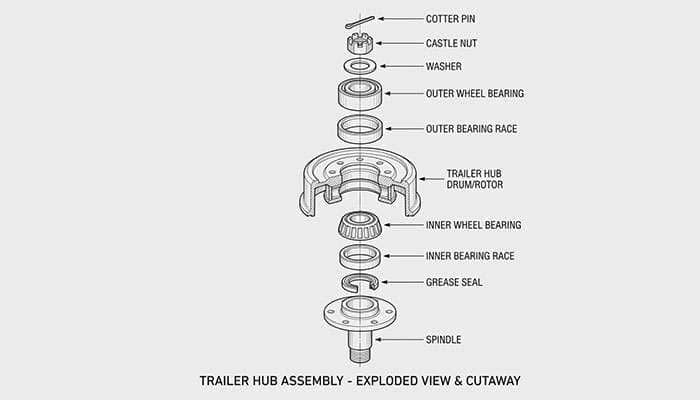
Trailer bearings need regular greasing to reduce friction between the wheel and axle. Without proper lubrication, bearings overheat quickly and can cause wheel seizure or detachment while driving.
Most trailers require bearing greasing every 10,000-12,000 miles or once per season minimum. Boat trailers with smaller wheels need more frequent attention - sometimes every 2,000 miles. We carry the best selection of aftermarket trailer wheels at discount prices at Performance Plus Tire for reliable, long-lasting performance.
Watch for squealing noises, excessive heat in wheel hubs, or unusual vibration - these are warning signs that your bearings need immediate attention.
Selecting the wrong wheels costs money and creates safety risks. Even careful measuring doesn't guarantee success when you overlook critical details that affect wheel compatibility.
Many trailer owners assume all 5-lug patterns are identical—they're definitely not! Measuring from the tire sidewall instead of the wheel rim leads to incorrect measurements. The most popular trailer wheel bolt pattern is 5 on 4-1/2 inch, but several variations exist that look nearly identical.
Older trailers present another challenge. Worn lug holes can throw off your measurements. When lug holes become oval-shaped from years of use, getting accurate bolt pattern measurements becomes much more difficult.
Load ratings determine how much weight each tire can safely support. The load range shows tire construction strength—B equals 4-ply, C equals 6-ply, and D equals 8-ply. Using tires with insufficient load rating for your trailer's weight can lead to dangerous blowouts.
Hub bore size gets overlooked frequently. The wheel's center opening must match your hub size to prevent vibrations and ensure proper alignment. Wrong hub bore size means wheels that technically bolt on but create handling problems and premature wear.
The 60/40 rule requires 60% of trailer weight positioned forward of the axle and 40% behind. This distribution maintains proper tongue weight (10-15% of total load) and prevents dangerous trailer sway.
The 80% rule means never exceeding 80% of your vehicle's maximum towing capacity. This safety margin accounts for measurement errors, shifting loads, and emergency braking situations. Heavy loads strain your engine, transmission, and brakes while making your vehicle harder to control.
We carry the best selection of trailer wheels at the lowest prices. Our huge selection includes all the latest designs and proper load ratings for safe towing performance.
Understanding proper trailer wheel fitment is essential for safe towing and avoiding costly mistakes. Here are the critical insights every trailer owner needs:
• Bolt pattern is king: Measure the number of lugs and circle diameter precisely - even small errors can result in wheels that won't fit your trailer hub.
• Even vs. odd lug measuring differs: For even lugs (4,6,8), measure straight across center; for odd lugs (5), use center-to-edge or adjacent bolt methods.
• Not all 5-lug patterns are identical: Common patterns include 5 on 4.5" and 5 on 5", so verify your exact measurements before purchasing.
• Load ratings and clearance matter: Check tire load range (B, C, or D), wheel offset, and hub bore size to ensure proper weight capacity and clearance.
• Follow the 60/40 and 80% towing rules: Keep 60% of trailer weight forward of axle and never exceed 80% of your vehicle's towing capacity for safe operation.
Proper wheel fitment goes beyond just bolt patterns - it encompasses load ratings, offset measurements, and adherence to towing safety guidelines. Taking time to measure accurately and understand these factors prevents dangerous situations and ensures your trailer performs reliably for years to come.
To determine the correct wheel size, measure the wheel diameter from bead seat to bead seat and the width between opposite bead seats. For example, a "14 X 5-1/2" wheel has a 14-inch diameter and 5.5-inch width. Also, check the rim contour stamp (like "JJ" or "K") to ensure you match the existing profile.
The most common bolt pattern for trailer wheels is 5 on 4.5 inches (also written as 5x4.5 or 545). However, it's crucial to measure your specific trailer's bolt pattern accurately, as there are several variations, especially for 5-lug wheels.
Yes, trailer wheels should be balanced. While the impact on ride comfort may be less noticeable than in passenger vehicles, balanced trailer tires run cooler and smoother. This reduces the risk of blowouts, improves fuel efficiency, and extends tire life.
Trailer bearings should be greased every 10,000-12,000 miles or at least once per season. However, boat trailers with smaller wheels may need more frequent attention, sometimes every 2,000 miles. Regular greasing reduces friction and prevents overheating, which could lead to wheel seizure or detachment.
The 60/40 rule states that 60% of the trailer's weight should be positioned forward of the axle and 40% behind. This distribution helps maintain proper tongue weight (typically 10-15% of the total load) and prevents dangerous trailer sway, ensuring safer towing.