
Every passenger vehicle in the United States has included TPMS sensors since 2008. These small but crucial components monitor tire pressure levels continuously, serving as an essential safety system that protects drivers and passengers on every journey.
TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System) sensors work around the clock to alert drivers when tire pressure drops below safe levels. The system's purpose is clear and critical – detecting dangerous tire pressure conditions before they create serious safety hazards. TPMS sensors prevent tire blowouts and flats during driving, maintain optimal fuel efficiency, extend tire lifespan, and ensure your vehicle handles and brakes at peak performance.
When tires lose air pressure, the consequences affect both safety and your budget. Under-inflated tires reduce handling capability, put extra strain on your braking system, decrease fuel economy, cause uneven tire wear, and can lead to dangerous overheating and blowouts. TPMS monitoring helps maintain correct tire pressure, delivering significant benefits for both vehicle safety and long-term savings.
We'll guide you through how these essential safety systems work, why every driver needs properly functioning TPMS sensors, and the best practices for maintaining them to ensure maximum vehicle safety and performance.

Image Source: Urb's Garage
Tire Pressure Monitoring System technology has evolved from luxury European vehicles in the 1980s to become standard safety equipment. The US TREAD Act passed in 2000 accelerated widespread adoption, making TPMS an essential component of modern vehicle safety systems.
TPMS operates as an electronic monitoring network that tracks air pressure inside each tire continuously. Your dashboard receives real-time pressure data displayed through gauges, pictogram displays, or warning lights.
Modern TPMS sensors integrate several critical components:
Pressure sensor for accurate readings
Microcontroller for data processing
Radio frequency transmitter for wireless communication
Battery management system for long-term operation
Temperature sensor for environmental compensation (select models)
These components function together to detect pressure variations and provide immediate alerts when unsafe conditions develop.
TPMS delivers measurable benefits through early detection of tire pressure problems. Research demonstrates the significant impact of proper tire inflation:
Fuel economy improves by 20% in passenger cars and 30% in commercial vehicles when tires maintain proper pressure
Tire lifespan extends by approximately 25% with consistent pressure monitoring
Vehicle handling and braking performance remain at optimal levels
The European Commission study by TRL shows TPMS has reduced traffic accidents by approximately 30%. Additionally, the European Union reports that under-inflated tires waste over 20 million liters of fuel annually and generate more than 2 million tons of excess CO2 emissions.
Two distinct TPMS technologies offer different approaches to pressure monitoring:
Direct TPMS (dTPMS) uses physical pressure sensors mounted inside each tire to measure actual pressure. These sensors transmit precise data wirelessly to the vehicle's central control unit. Direct systems provide accurate, real-time readings for individual tires and can detect simultaneous pressure loss across multiple tires.
Indirect TPMS (iTPMS) operates without physical pressure sensors, instead using wheel speed sensors from the anti-lock braking system. When a tire loses air, its smaller diameter causes faster rotation compared to properly inflated tires. Research indicates 69% of drivers prefer systems that don't require manual reset procedures.
Your specific driving needs and vehicle requirements determine which system provides the best performance for your situation.
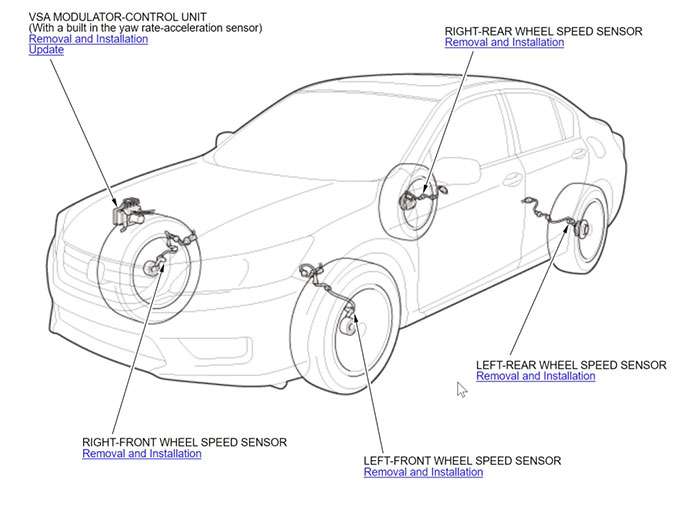
Image Source: arts automotive
TPMS sensors function as your vehicle's first line of defense against tire-related hazards. These systems provide protection that extends far beyond basic pressure monitoring, creating multiple layers of safety and performance benefits.
Tire blowouts create serious safety hazards, particularly at highway speeds. Research shows that approximately 40% of unexpected tire failures result from underinflation. TPMS delivers critical early warnings before pressure reaches dangerous levels, detecting underinflation long before visual inspection would reveal the problem.
A properly functioning TPMS reduces the chance of crashes due to tire issues by an estimated 55%. This early detection allows drivers to address pressure problems before they escalate to catastrophic failures, providing essential protection for you and your passengers.
Proper tire pressure delivers substantial economic benefits. Minor pressure deficits create significant fuel consumption increases – even a 0.3 bar drop can raise fuel consumption by 1.5%, while a 0.5 bar deficit might increase consumption by up to 5%.
The U.S. Department of Energy reports approximately a 0.2% reduction in fuel economy for every 1 PSI drop in average tire pressure. Over time, a TPMS saves a typical passenger car 9.32 gallons of fuel during its first eight years of operation. These savings add up to hundreds of dollars in your pocket.
Improper inflation creates distinctive wear patterns that shorten tire lifespan. Underinflated tires wear faster on their edges, while overinflated tires show accelerated center tread wear. TPMS helps maintain optimal pressure, ensuring even wear distribution across the entire tread surface.
This balanced wear pattern significantly extends tire lifespan. Underinflation alone can reduce tire life by approximately 25%, making TPMS monitoring a smart investment in tire longevity.
Properly inflated tires deliver optimal road contact for maximum vehicle control. Correct pressure ensures tires maintain their designed shape, providing superior traction during cornering and emergency maneuvers. Underinflated tires reduce handling capability, strain braking systems, and increase stopping distances.
Properly inflated tires also excel in adverse weather conditions, offering enhanced grip on wet or slippery surfaces when you need it most.

Image Source: AutoZone.com
Understanding TPMS sensor maintenance helps you get the most from these safety systems. These components require minimal attention but knowing their limitations ensures your vehicle's tire monitoring system performs reliably.
TPMS sensors use non-replaceable lithium batteries that typically provide 5-10 years of service. Your driving habits directly impact battery longevity—steady highway driving preserves power, while frequent stop-and-go conditions increase transmission activity and drain batteries faster. Temperature extremes also affect battery performance, with colder environments generally extending battery life compared to consistently hot climates.
Watch for a flashing TPMS light that blinks for 60-90 seconds when you start your vehicle. This pattern signals a failing sensor battery rather than low tire pressure. While you can replace individual sensors, we recommend changing all four sensors when the first one fails, since the remaining sensors will likely need replacement within a short timeframe.
New sensors require your vehicle to "learn" their unique identification codes. Three relearn methods are available:
Stationary: Uses specific key sequences designated by your vehicle manufacturer
OBD: Connects diagnostic equipment directly to your vehicle's computer system
Automatic: Requires driving at manufacturer-specified speeds for set time periods
Many service issues stem from skipping essential maintenance steps. Technicians often forget to replace service kits that include the cap, washer, nut, and valve core when mounting tires. Another frequent oversight is failing to perform the relearn procedure after tire rotation. Using outdated diagnostic software or rough handling during tire service can damage sensors unnecessarily.
Our expert team understands these critical maintenance requirements and ensures proper TPMS service to keep your safety systems functioning at peak performance.
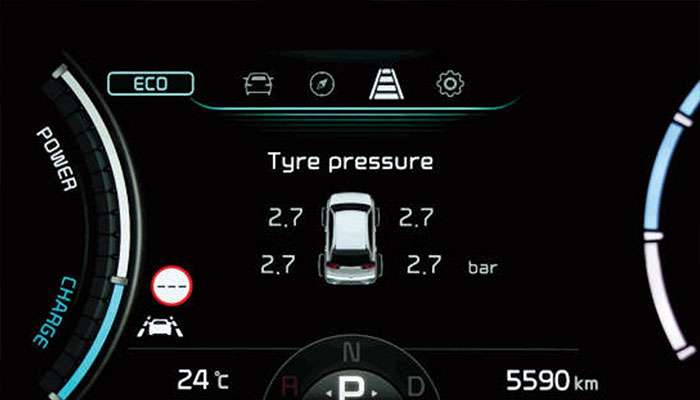
Image Source: kingbolen
That yellow warning light on your dashboard requires attention, but it doesn't signal disaster. Understanding what your TPMS indicators mean helps you respond appropriately and maintain your vehicle's safety systems.
The illuminated TPMS light tells you at least one tire has dropped significantly below recommended pressure levels. Check all tires immediately when this light appears, including the spare. Low tire pressure creates serious road hazards, contributing to 738 tire-related crash fatalities in 2017.
A solid light means one or more tires are at least 25% below recommended pressure. A flashing light (typically for 60-90 seconds before staying solid) indicates a system malfunction. This flashing pattern usually means sensors can't communicate with your vehicle, often due to damage, dead batteries, or improper sensor installation.
Once you've properly inflated your tires, the light should turn off automatically. If it doesn't, try these steps:
Drive at 50 mph for approximately 10 minutes
Turn your key to the "on" position (engine off), then hold the TPMS reset button until the light blinks three times
Check your owner's manual for vehicle-specific reset procedures
Professional help becomes necessary when the light persists after reset attempts, continues flashing, or keeps returning. Persistent TPMS warnings typically indicate sensor battery failure (usually after 7-10 years), damaged sensors, or system malfunctions that require specialized diagnostic equipment.
TPMS sensors represent one of the most important safety advances in modern vehicles. These essential components work continuously to protect drivers and passengers while delivering significant economic benefits through improved fuel efficiency and extended tire life.
The federal requirement for TPMS in all passenger vehicles since 2008 reflects the critical role these sensors play in road safety. When functioning properly, TPMS systems prevent dangerous tire failures while helping you save money at the gas pump and on tire replacement costs.
Understanding your TPMS system transforms that yellow dashboard light from an annoyance into a valuable safety alert. The system's ability to detect pressure problems before they become visible makes it an indispensable part of vehicle maintenance. Regular attention to TPMS warnings and proper sensor maintenance ensures these safety systems continue protecting you throughout their 5-10 year lifespan.
We recommend treating TPMS sensors as essential safety equipment rather than optional technology. When that warning light appears, address it promptly - your safety and your wallet will benefit from maintaining proper tire pressure. Professional diagnostics become necessary when simple troubleshooting doesn't resolve persistent warnings, but the investment in properly functioning TPMS sensors pays dividends in safety, performance, and cost savings.
At Performance Plus Tire, we understand the importance of properly functioning TPMS sensors for vehicle safety and performance. Our experienced technicians can help diagnose TPMS issues, replace failing sensors, and ensure your vehicle's tire monitoring system operates at peak efficiency. Remember, these silent guardians work tirelessly to keep you safe - they deserve your attention and proper maintenance in return.
TPMS sensors are mandatory safety guardians that have been protecting drivers since 2008, continuously monitoring tire pressure to prevent dangerous blowouts and accidents.
• TPMS prevents up to 55% of tire-related crashes by detecting dangerous pressure drops before they become visible or catastrophic • Proper tire pressure maintained through TPMS monitoring can improve fuel economy by up to 5% and extend tire life by 25% • TPMS sensor batteries last 5-10 years; a flashing warning light for 60-90 seconds indicates system malfunction requiring professional attention • Direct TPMS provides real-time pressure readings for each tire, while indirect systems use wheel speed sensors to detect pressure differences • Never ignore TPMS warnings - even minor underinflation reduces handling capability and increases stopping distances significantly
Understanding your TPMS system transforms it from an annoying dashboard light into a valuable safety partner that protects your life, saves money, and extends your vehicle's performance capabilities.
TPMS sensors continuously monitor tire pressure and alert drivers when it falls below recommended levels. This helps prevent tire blowouts, improves fuel efficiency, extends tire life, and enhances vehicle handling and braking performance.
TPMS sensors typically need replacement every 5-10 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions. The primary indicator for replacement is a flashing TPMS light that continues for 60-90 seconds during vehicle startup.
Direct TPMS uses physical pressure sensors inside each tire to measure pressure accurately, while indirect TPMS relies on wheel speed sensors to detect pressure differences based on tire rotation rates.
After proper inflation, the TPMS light usually deactivates automatically. If not, try driving at 50 mph for about 10 minutes or consult your owner's manual for vehicle-specific reset procedures.
Seek professional diagnostics if the TPMS light persists after reset attempts, continues flashing, or repeatedly returns. This may indicate sensor battery failure, damaged sensors, or system malfunctions requiring specialized equipment.