
Those numbers printed on your tire sidewall aren't random markings—they tell the complete story of your tire's dimensions and performance characteristics. The aspect ratio, in particular, directly controls how much cushioning your vehicle has against bumps and road irregularities.
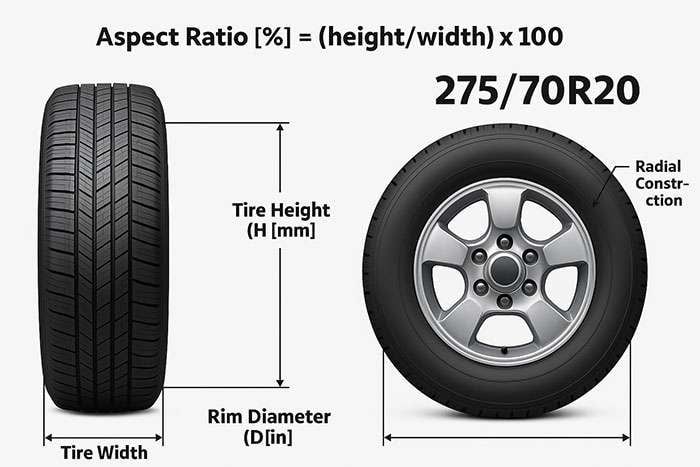
Tire aspect ratio represents the height of the tire's sidewall expressed as a percentage of its width. When you see a tire with an aspect ratio of 65, it means the sidewall height is 65% of the tire's width. This tire size measurement essentially determines how tall your tire will be in the final product. For example, if the aspect ratio is 90, your tire's cross-sectional height equals 90% of its width.
Understanding tire aspect ratio is crucial because it significantly affects your driving experience. Tires with taller sidewalls have more rubber to cushion your vehicle during drives, while shorter sidewalls provide sharper steering and better controllability. Tires with an aspect ratio of 40 or 30 are classified as low profile, while standard tires typically have ratios around 60 or 70.
We'll decode these important sidewall numbers, explain how to calculate tire dimensions, and help you understand how different aspect ratios affect your vehicle's performance and comfort.
Your tire's sidewall displays a series of numbers and letters that contain valuable information about your tire's dimensions and performance characteristics. These markings follow a standardized format that makes sense once you know how to read them.
The tire aspect ratio appears as the second number in the tire size designation on the sidewall. This number represents the height of the tire's sidewall as a percentage of its width. For instance, in a tire size like 215/65R16, the aspect ratio is 65, which means the sidewall height is 65% of the tire's width.
Consider a tire with width 215mm (approximately 8.46 inches). With an aspect ratio of 65, the sidewall height would be 5.5 inches (8.46 × 0.65). Tires with aspect ratios of 55 or less typically indicate shorter sidewalls designed for improved steering response and better handling.
Breaking down the 235/80R16 tire size reveals each component's meaning:
For this particular tire, we can calculate the sidewall height by converting 235mm to inches (approximately 9.25") and multiplying by 0.80, which gives us about 7.4 inches for the sidewall height. This isn't the total tire height - to find that, we would double the sidewall height (7.4" × 2 = 14.8") and add the wheel diameter (16"), resulting in a total tire diameter of approximately 30.8 inches.
The width measurement is crucial since the aspect ratio is calculated as a percentage of this width. Even with identical aspect ratios, wider tires will have taller sidewalls.
This relationship directly impacts tire performance. The taller the sidewall (higher aspect ratio), the more rubber there is to cushion your ride. Lower aspect ratio tires provide enhanced cornering and braking capabilities but deliver a firmer ride.
Understanding this relationship helps you make informed choices about replacement tires, as staying within your vehicle's recommended specifications ensures proper handling, safety, and fuel efficiency.
Understanding tire dimension calculations helps you make informed decisions when selecting replacement tires. These sidewall numbers follow precise mathematical relationships that determine your tire's final size and performance characteristics.
The aspect ratio calculation starts with the tire size code printed on your sidewall. When you see a tire size like 235/80R16, the aspect ratio (80) represents the sidewall height as a percentage of the tire's width. The sidewall height equals the section width multiplied by the aspect ratio percentage.
Calculate sidewall height using these steps:
For a 215/65R16 tire, the sidewall height calculation would be: 215mm × 0.65 = 139.75mm
Tire measurements mix metric and imperial units, making conversion necessary. Convert millimeters to inches by dividing by 25.4 (the number of millimeters per inch):
215mm ÷ 25.4 = 8.46 inches
For our 215/65R16 example: 8.46 inches × 0.65 = 5.5 inches sidewall height
Using the 235/80R16 tire: 235mm ÷ 25.4 = 9.25 inches 9.25 inches × 0.80 = 7.4 inches sidewall height
The total tire diameter combines the wheel diameter plus twice the sidewall height (since there's a sidewall both above and below the wheel). The formula is:
Total tire diameter = (2 × sidewall height) + wheel diameter
Using our 235/80R16 example:
This calculation is essential when considering different tire sizes, as it affects speedometer accuracy, ground clearance, and overall vehicle performance. Each revolution of a larger-diameter tire covers more distance, causing your vehicle to actually travel faster than your speedometer indicates.
The aspect ratio directly influences your vehicle's performance dynamics in ways you'll feel every time you drive. This critical number affects your daily driving experience more than most drivers realize.
Tires with higher aspect ratios (70-80) feature taller sidewalls that act as natural shock absorbers, cushioning your ride over bumps and road irregularities. Lower aspect ratios (50 or below) provide stiffer sidewalls with less flex, delivering sharper steering response and improved handling precision. This creates a fundamental choice between plush comfort and sporty control.
The difference is noticeable immediately. High aspect ratio tires smooth out road imperfections, making long drives more comfortable. Low aspect ratio tires transmit more road feel directly to the steering wheel, giving you better feedback about what your vehicle is doing.
Your tire's aspect ratio affects your wallet at the gas pump. Lower aspect ratio tires typically generate higher rolling resistance, potentially decreasing fuel economy. This occurs because wider tires with shorter sidewalls create more friction against the road surface. Tires with taller sidewalls often contribute to better fuel efficiency due to reduced rolling resistance.
Performance enthusiasts often prefer lower aspect ratios due to their superior braking capabilities and cornering grip. The stiffer sidewalls maintain better contact with the road during aggressive maneuvers. Braking, cornering, and overall maneuverability improve noticeably with smaller aspect ratio tires. This performance advantage comes at a cost—faster tread wear rates and decreased traction in winter conditions.
When you need maximum stopping power or precise cornering, low aspect ratio tires deliver the performance. For everyday driving comfort and fuel savings, higher aspect ratios make more sense.
Selecting the appropriate tire aspect ratio requires balancing performance needs with driving conditions. The right choice depends on your specific vehicle requirements and driving habits.

Generally, tires with an aspect ratio below 50 are classified as low-profile. Although this definition has evolved over time, today's automotive standards typically categorize tires with aspect ratios of 40 or 30 as low-profile, whereas standard tires usually feature ratios around 60 or 70.
Choose higher aspect ratios when comfort and efficiency are your priorities. Taller sidewalls (higher aspect ratios) deliver superior fuel economy plus better absorption of road shocks. Additionally, these tires handle larger loads effectively, making them ideal for family vehicles, long-distance driving, or when frequently traveling on rough roads.
Incorrect tire sizes create serious problems for your vehicle. They affect critical vehicle systems including speedometers, anti-lock brakes, and stability control. Oversized tires might rub against wheel wells, causing premature wear both to tires and vehicle components. Most importantly, incorrect sizing compromises safety by altering braking performance, especially in wet conditions.
Locate your recommended tire specifications through several reliable sources. Check the sticker on your vehicle's door jamb, which lists manufacturer-approved tire sizes. The owner's manual always contains this critical information. Remember that the maximum pressure displayed on the tire sidewall isn't necessarily the recommended pressure—refer to your vehicle's placard instead.
Understanding tire aspect ratio is essential for making smart tire choices. Those sidewall numbers tell you exactly how your tires will perform on the road, affecting everything from ride comfort to handling precision.
The aspect ratio fundamentally determines how much cushioning your vehicle has against road irregularities. Higher aspect ratios (60-80) provide more comfort and better fuel efficiency, whereas lower aspect ratios (below 50) deliver sharper handling and improved cornering abilities. This knowledge helps you make informed decisions when replacing tires.
We've learned how to calculate tire dimensions using the aspect ratio formula. The sidewall height equals the tire width multiplied by the aspect ratio percentage. A 235/80R16 tire has a sidewall height of approximately 7.4 inches and a total diameter of about 30.8 inches.
Using the wrong aspect ratio creates serious problems with vehicle systems, including speedometer accuracy, anti-lock brakes, and stability control. Always consult your vehicle's door jamb sticker or owner's manual for manufacturer-approved tire sizes.
The right tire aspect ratio balances your specific needs for comfort, performance, and driving conditions. Whether you prioritize a smooth ride quality for daily commuting or prefer responsive handling for spirited driving, the aspect ratio significantly influences your overall driving experience. You can now confidently decode those sidewall numbers and select tires that perfectly match your vehicle and driving preferences.
Understanding tire aspect ratios empowers you to make informed decisions about your vehicle's performance, comfort, and safety.
• Aspect ratio is sidewall height as percentage of tire width - In 235/80R16, the "80" means sidewall height equals 80% of the 235mm width • Higher ratios (60-80) prioritize comfort and fuel efficiency while lower ratios (below 50) deliver sharper handling and cornering control • Calculate total tire diameter by doubling sidewall height and adding wheel diameter - Essential for maintaining speedometer accuracy and vehicle systems • Wrong aspect ratio compromises safety systems including ABS, stability control, and can cause tire rubbing against wheel wells • Always check your vehicle's door jamb sticker or owner's manual for manufacturer-approved tire sizes rather than guessing or copying other vehicles
The right aspect ratio balances your specific driving needs - whether you value ride comfort for daily commuting or responsive performance for spirited driving.
The tire aspect ratio represents the height of the tire's sidewall as a percentage of its width. For example, in a tire size 215/65R16, the aspect ratio is 65, meaning the sidewall height is 65% of the tire's width.
Higher aspect ratios (60-80) provide more comfort and better absorption of road shocks, while lower aspect ratios (below 50) offer sharper handling and improved cornering abilities but a firmer ride.
Generally, tires with an aspect ratio below 50 are classified as low-profile. Today's automotive standards typically categorize tires with aspect ratios of 40 or 30 as low-profile, while standard tires usually have ratios around 60 or 70.
To calculate the total tire diameter, double the sidewall height and add the wheel diameter. For example, with a 235/80R16 tire, the total diameter would be approximately 30.8 inches.
You can find the recommended tire specifications on the sticker located on your vehicle's door jamb or in the owner's manual. These sources provide manufacturer-approved tire sizes for your specific vehicle model.